Overview
This document is a quick dive into digital environments for places like farms or airfields that have large areas and no power supply to the remote areas. The purpose of this document is to highlight what off the self components can be used and how they can be plugged together to build up a digital picture. A basic components are ...- Data Collection
- Temperatures
- Location
- Acceleration
- Radio Frequencies
- Data Processing
- Embedded Systems
- Micro Controllers
- Power
- Storage
- Generation
- Data Communication
- GSM
- Lora
- Wifi
- Data Collection and Analysis
- Live
- Historical
- Argumented
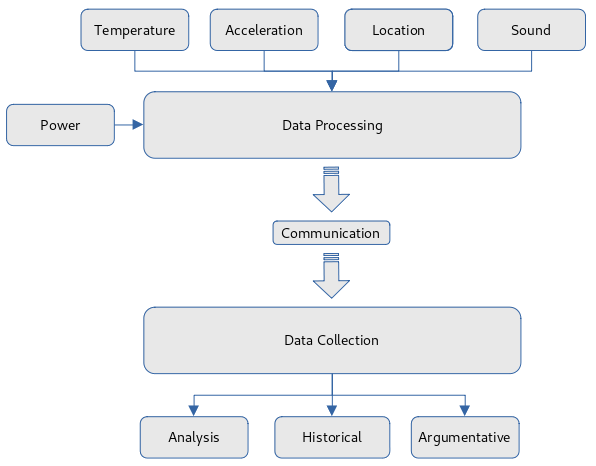
Data Collection
To collect data you first need to digitize the thing your collecting. The table below provides some examples of devices that collect specific pieces of information.
| Data | Device |
| Temperatures / Humidity / Pressures | BME280 |
| Wind Speed and Direction | Adafruit Anemometer |
| Acceleration / Rotation | MPU-9250 9-Axis Gyro, Accelerometer, and Magnetometer |
| Radio Frequencies | Software Defined Radio such as a Neolec or HackRF One |
| Distances | VL53L0X Time-of-Flight (ToF) Laser Distance Sensor |
| Positions | U-blox NEO-6M GPS Module |
| Torque | Honeywell TMS9250 |
| Sound | USB Sound Card |
| Salinity | EZO-EC Sensor |
Data Processing
Once the data input devices have been selected they can be plugged into the data processing unit which can be either a embedded system such as a Raspberry Pi Zero or a ESP32 micro controller. Its worth noting that a micro controller will use less power than an embedded system but comes at the cost of not being able to easily plug in some input devices such as a software defined radios.
Power
Power is the biggest drawback when it comes to collecting data from remote places but this can usually be overcome by using a combination of batteries and energy producing devices such as solar panels or turbines.Data Communication
After collecting the data you'll want to transport it and depending on your needs will depend on what form of communication will be used. Smart phones contain a few forms of communication methods such as GSM, Bluetooth and Wifi but other forms such as LoRaWan can also be used. The whole purpose of transporting the data is so it can be collected centrally.
Data Analyzes
There are three types of data analyses.- Live
- Historical
- Argumentative
Core Values
- Locally manufactured products preferred, Raspberry Pi's in mind
- Responsible sourced components, if its now available locally then may a neighbor will have it
- Locally employed people
- Apprenticeship and training schemes
- Product longevity, things should be built to last and not fail for profit
- Rigorous testing with routines and Tested products